🔔 Admissions Open 2026–27 | Limited 10 Students per Batch
A Better Way to Learn
for Nursery to
Grade 12
Vikalp India is an experiential, child-centric online school that combines structured academics with hands-on, activity-based learning — building confidence, curiosity, and real understanding beyond rote memorization.
98%
Parent SatisfactionFrom 1000+ parents
20,000+ Learners
15+ Years in Experiential Learning
300+ Trained Facilitators
Aligned with NEP 2020
Find the right fit for your child
Whether your child is starting school or exploring new skills, Vikalp has a path designed just for them.
Preschool
Nursery, LKG, UKG (3-6 years)
Play-based learning that sparks curiosity and prepares your child for school with joy, not pressure.
School
Primary to Grade 12
A full school experience with activities, & mentorship that turns learning more exciting.
Skills
Coding, Languages, Music
Help your child discover their strengths through skill-building classes led by expert mentors.
Does this sound familiar?
You want the best for your child. But traditional online classes feel like they are falling short.
My child is bored in online classes
Too much screen time, too little engagement
Memorising without understanding
No personal attention from teachers
Not just another online school
Vikalp is built on 15+ years of experiential education research. Every class is designed to make children think, create, and grow.
Activity-Based Learning
Children learn by doing — through experiments, projects, and real-world exploration. Not passive listening.
Facilitators, Not Lecturers
Our trained facilitators guide children to discover answers themselves, building confidence and critical thinking.
Personalised Learning
Every child is unique. We adapt pace, style, and content to match how your child learns best.
Physical + Digital Tools
Learning goes beyond the screen with activity kits, worksheets, and hands-on materials delivered to your home.
Choose the right path for your child
Three focused pathways, each designed to bring out the best in every learner.

Online School
Nursery to Grade 12
A complete, recognised school program delivered through activity-based methods with personal mentorship.

Skill Classes
Coding, Robotics, Public Speaking & more
Structured skill-building programs that prepare children for the real world beyond textbooks.

Languages
English, Hindi, French, Spanish & more
Interactive language learning that builds fluency through conversation, stories, and cultural immersion.
Real parents. Real outcomes.
Thousands of families trust Vikalp with their children's education journey.

In traditional classrooms, many students hesitate to speak up. At VIKALP, every student is heard. Teachers use discussion-based learning, where ideas are exchanged freely.
Smitha
Parent
With VIKALP’s flexible structure and online format, students can pursue hobbies, family time, or personal projects alongside academics. One of the biggest transformations parents notice is balance.
Joseph Allwin Dhas
Parent
VIKALP’s focus on small batches, individual guidance, and emotional support makes it more than just a school—it’s a community that helps students prepare for life beyond academics.
Safina
Parent
At VIKALP, children learn through play and discovery. Tools like math kits, dominoes, phonics cards, and storytelling activities make lessons interactive and engaging. My child gets excited.
Saurabh Siddiqi
ParentACCREDITED ONLINE SCHOOL
Featured In:
How admissions work
A simple, transparent process designed to find the best fit for your child. No pressure, no rush.
Book Free 15-min Counselling
Speak to our academic counsellor about your child's needs, interests, and learning goals.
Complete Child Assessment
A friendly, stress-free assessment to understand your child's current level and learning style.
Program Recommendation
We recommend the best-fit program based on the assessment and your family's preferences.
Admission & Onboarding
Quick, hassle-free onboarding with a dedicated coordinator to get your child started.
Not sure which program is right
for your child?
Speak to our academic counsellor — it's free. No commitments,
no pressure. Just an honest conversation about your child's learning needs.
Trusted by 20,000+ parents across India
Frequently asked questions
Is online school recognized?
Yes — It Offers Recognized Curriculum Options
Vikalp Online School provides education aligned with Indian curricula (NCERT) and offers pathways for students to appear for recognized board examinations through either:
- NIOS (National Institute of Open Schooling) — India’s official open schooling board, recognized by the Government of India and widely accepted for certification. Students can register with NIOS and take Class 10/12 board exams.
- CBSE (Central Board of Secondary Education) — the national board for thousands of Indian schools. Vikalp says students can choose CBSE pathways (though details often involve registering with an authorized CBSE-affiliated study centre or partner).
The curriculum and certification options offered link to recognized Indian boards — so students who complete NIOS or CBSE paths through Vikalp can receive legitimate board certificates.
Is Vikalp aligned with NEP 2020?
Vikalp Online School emphasizes an experiential, activity-based learning model (learning by doing, small class sizes, student participation, critical thinking and exploration). This pedagogical approach is more modern compared to traditional rote learning.
📌 2. NEP 2020 Focus Areas
The National Education Policy 2020 encourages:
- Holistic, learner-centric education (critical thinking, experiential and activity-based learning)
- Flexibility in curricula and pedagogy
- Focus on foundational literacy and numeracy, holistic development, and digital/distance learning support.
These broad NEP principles encourage teaching methods that go beyond rote memorization — including experiential and activity-centric approaches — which aligns philosophically with Vikalp’s methods.
How is Vikalp different from regular online classes?
1️⃣ It’s Experiential, Not Just Virtual
Most online schools simply move traditional classrooms to Zoom — lectures, slides, homework.
Vikalp is built on experiential learning.
Students learn through activities, thinking exercises, problem-solving, and concept discovery. Teachers act as facilitators, not just content deliverers.
2️⃣ Focus on Concept Mastery, Not Syllabus Coverage
Regular online schools focus on completing the curriculum.
Vikalp focuses on deep conceptual clarity — ensuring students understand why something works, not just what to write in exams.
3️⃣ Small, Interactive Learning Environment
Many online schools run large batches.
Vikalp emphasizes small groups and individual attention, allowing personalized guidance and active participation.
4️⃣ Blended Physical + Digital Learning
Regular online schools are screen-heavy.
Vikalp integrates hands-on learning tools and offline activities along with digital sessions — making learning more engaging and effective.
5️⃣ Homeschool-Friendly Structure
Vikalp supports families who want structured schooling at home, with guidance and academic progression — not just classes.
How much screen time is involved?
At Vikalp, learning is intentionally designed so that students are not continuously looking at a screen.
A typical class follows a mixed-media structure:
- It often begins with a hands-on activity to introduce or explore a concept.
- This is followed by teacher guidance and discussion, where students listen, reflect, and interact.
- Students then move to offline work — completing exercises in their physical workbooks or engaging in structured activities away from the screen.
Because each lesson is divided into these purposeful segments, screen exposure is naturally limited. Students are not staring at a monitor for the entire duration of the session.
The screen is used as a tool, not the classroom.
What support do parents get?
At Vikalp, parents are not passive observers — they are active partners in their child’s learning journey. The school ensures continuous communication, guidance, and support.
- Regular Academic Updates
Parents receive regular updates on follow-up work sent to students, ensuring they know what reinforcement or practice is expected at home. Progress reports provide clarity on academic performance and concept mastery.
- Holistic Development Updates
Vikalp keeps parents informed not only about academics but also about their child’s mental and socio-emotional development. Teachers share observations regarding confidence, participation, emotional well-being, and learning behavior.
Early Issue Identification & Remedial Action
If any academic, behavioural, or emotional concern arises, parents are promptly notified. The school provides clear remedial steps and structured intervention plans, ensuring timely support.
- Career Guidance Support
Career guidance is regularly offered to both students and parents, helping families make informed decisions about subject choices, board pathways, and future academic or professional directions.
- Detailed Parent-Teacher Meetings (PTMs)
During PTMs:
- Each child’s strengths and weaknesses are discussed in depth.
- Teachers and parents collaboratively review progress.
- Specific remedial plans and improvement strategies are outlined clearly.
- Open Communication Channels
Teachers remain accessible for discussions, clarifications, and guidance — fostering a transparent and supportive environment.
Can my child transition back to offline CBSE / ICSE schools later?
Yes. Students from Vikalp Online School can transition to offline CBSE or ICSE schools.
Vikalp follows the NCERT syllabus, ensuring that the curriculum remains aligned with the academic standards of both CBSE and ICSE boards. This alignment supports a smooth academic transition.
Upon request, Vikalp issues the required Transfer Certificate (TC) and Marksheet, which are valid documents and are accepted by schools following CBSE and ICSE boards.
Most offline schools conduct an entrance assessment or interaction for new admissions. Migration is generally straightforward provided:
- The student clears the entrance assessment
- Valid documentation (Transfer Certificate and Marksheet) is submitted
- Seats are available in the desired grade
As with any school transfer, final admission is subject to the receiving school’s policies. However, with proper documentation and academic continuity, students can transition smoothly.
How are assessments and progress tracked?
At Vikalp, assessment is structured, continuous, and growth-oriented. We follow a system of Continuous and Comprehensive Evaluation (CCE) — meaning students are not evaluated only once or twice a year. Assessment is an ongoing process integrated into everyday learning.
- Formative Assessment (Continuous Evaluation)
Our Formative Assessment tracks student performance throughout the learning process. It includes:
- Daily classroom participation
- Workbook exercises
- Submitted assignments
- Project work
- Quizzes and activity-based tasks
These markers help teachers understand how children are performing while concepts are still being formed, allowing early identification of gaps and timely intervention.
Formative assessment also includes observation of each child’s socio-emotional development, including confidence, participation, focus, and engagement.
- Summative Assessment (Periodic Evaluation)
The second component is the Summative Assessment, which consists of written tests conducted twice a year.
These tests evaluate:
- Concept retention
- Application skills
- Ability to summarize and express understanding clearly
📊 3. Diagnostic Reporting & Remedial Planning
The results of both Formative and Summative Assessments are combined to create a detailed diagnostic report.
This report:
- Highlights a child’s strengths
- Identifies areas needing improvement
- Suggests specific remedial actions
If any academic or socio-emotional “red flags” are observed, they are discussed transparently during the Parent-Teacher Meeting (PTM), along with structured improvement strategies.
SCHOOLS
IMPLEMENTING ACTIVITY BASED LEARNING
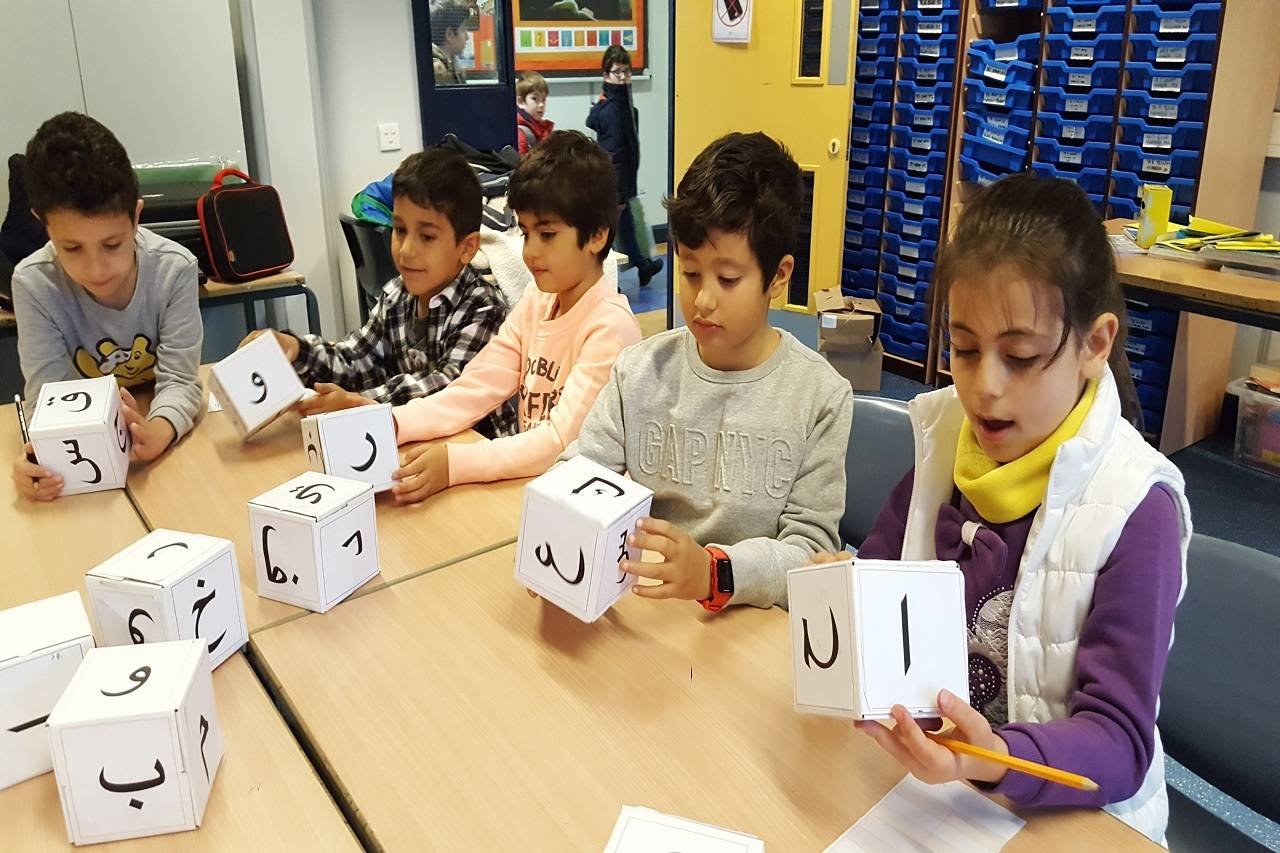
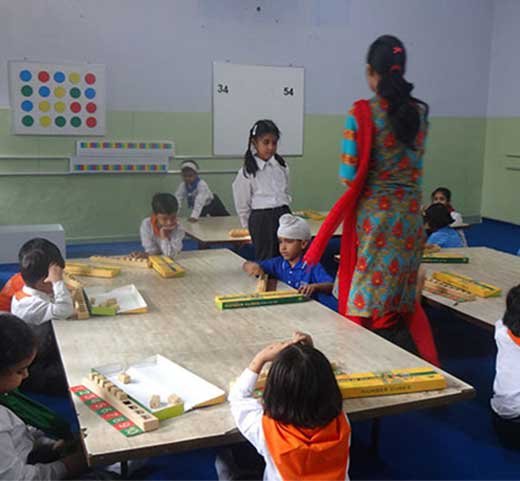




Activity-Based-Learning (ABL)
Enriching School Curriculum
We help schools to implement activity-based-learning in everyday teaching-learning practice. We set up an Activity Center inside schools. Students come to this center at regular intervals and Do and Learn. School Curriculum
Math Lab
Lab can be set up using the learning tools. Math concepts can to introduced using these tools. Children can play and discover mathematical concepts. Math Lab
Preschool Kit | ECD Kit
ECD kits or Pre-School Education (PSE) Kit are designed for early childhood development among kids. It contains lot of teaching-learning materials, puzzle cards, flipcharts etc. ECD Kit