Currently Empty: ₹0.00
Activity Based
Online School from Nursery to 12th Class
Are you looking for the best online homeschool program for your kid? You can choose the grade and enroll your child in an accredited K 12 Online School. It’s an Activity Based Online School for Pre-primary, Primary, Middle and Senior School. Your child can attend live interactive classes conducted by world class experiential educators. There are no lectures. Concepts are introduced using physical tools and children Do & Learn.
Partner Affiliation # 3430387
ACCREDITED ONLINE SCHOOL
PRESCHOOL
NURSERY, K1 - K2
PRIMARY SCHOOL
GRADE: 01 - 05
MIDDLE SCHOOL
GRADE: 06 - 08
SENIOR SCHOOL
GRADE: 09 - 12
Video Section

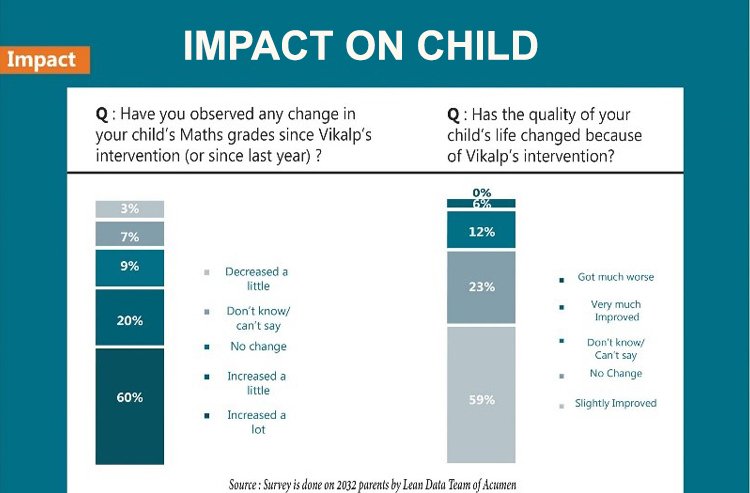
Impact on Your Child
Check the complete information on how Vikalp’s Experiential Learning impacts the Students.
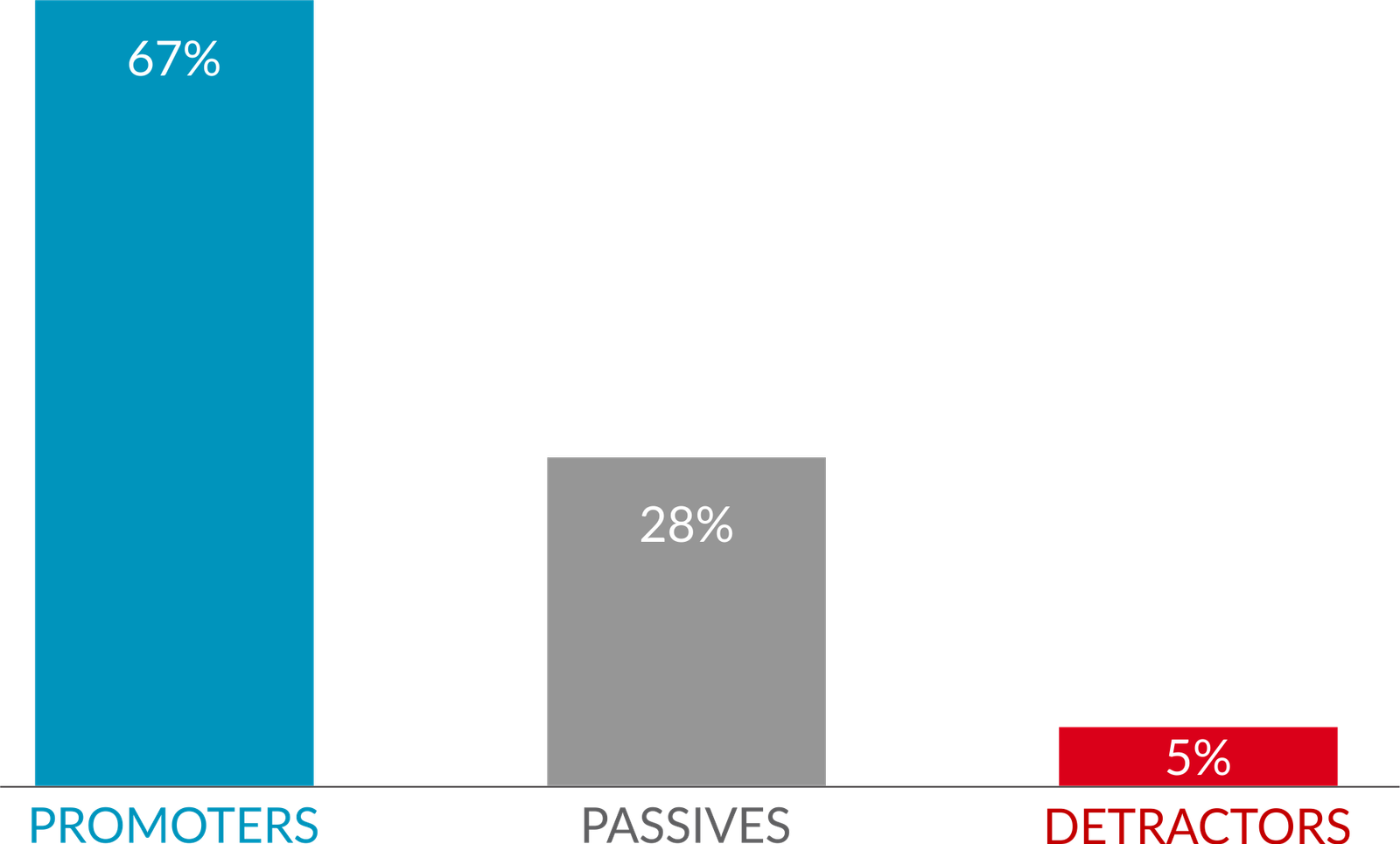
62% of our customers promote us…
Net Promoter Score
Our Net Promoter Score survey is done by Lean Data team of Acumen. Objective was to understand how satisfied our customers are. Net promoter scores were created by asking respondents to rate the likelihood they would refer Vikalp to someone else, using a scale from 0 to 10.
ABOUT US
Vikalp is the new Alternative in Education
We are trying to make a shift from blackboard teaching to experiential learning in everyday teaching-learning practice. Our Do and Learn approach cater to diverse learning needs of each child.
0 K
STUDENTS ENROLLED
0 K
CLASS COMPLETED
0 +
TEACHER-EDUCATORS
0 %
SATISFACTION RATE
School Section




Enable Schools to Implement
Activity-Based-Learning (ABL)
Enriching School Curriculum
We help schools to implement activity-based-learning in everyday teaching-learning practice. We set up an Activity Center inside schools. Students come to this center at regular intervals and Do and Learn. School Curriculum
Math Lab
Lab can be set up using the learning tools. Math concepts can to introduced using these tools. Children can play and discover mathematical concepts. Math Lab
Preschool Kit | ECD Kit
ECD kits or Pre-School Education (PSE) Kit are designed for early childhood development among kids. It contains lot of teaching-learning materials, puzzle cards, flipcharts etc. ECD Kit
LATEST ARTICLES
Get Latest Updates from Vikalp
Why do Vikalp students learn better?
Why do Vikalp students learn better? Vikalp Online School...
Why are Vikalp teachers different?
Why are Vikalp teachers different? Students have not been given many opportunities to think in public schools. Teachers in these…
Preparing Students for Future Jobs
Preparing Students for Future Jobs Students who are in school now, will hit the job market smetime between 2035 to…